Mechanism of the V24P (10-40) scavenger peptide.
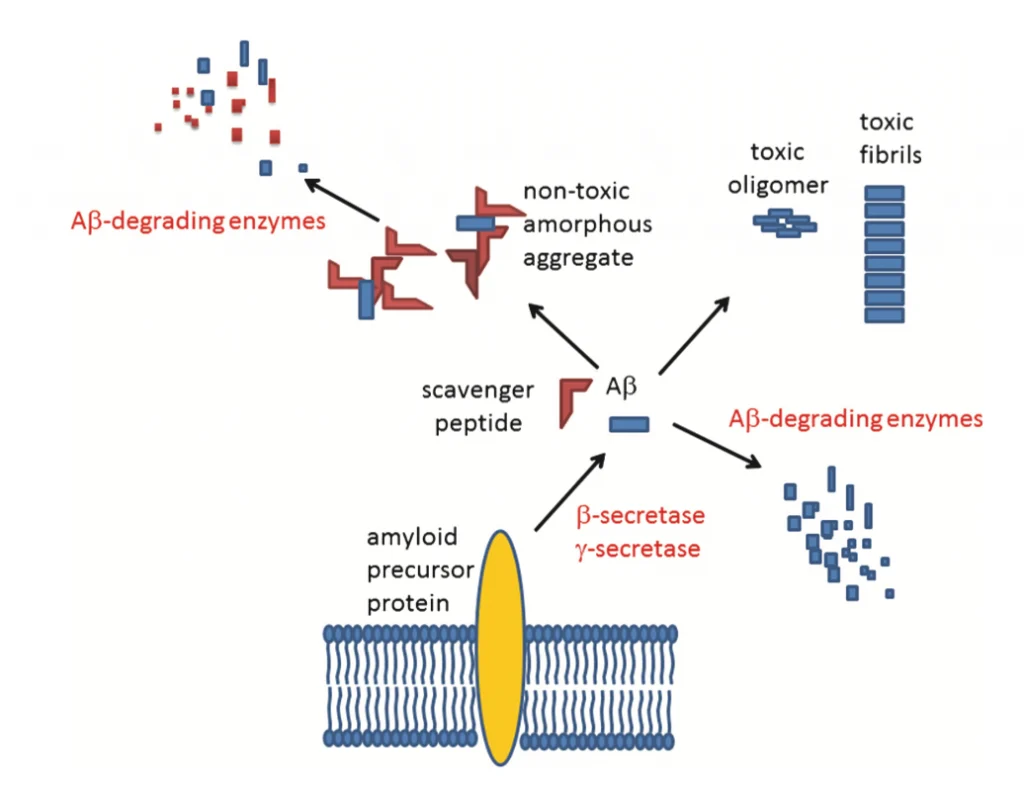
Figure 1.
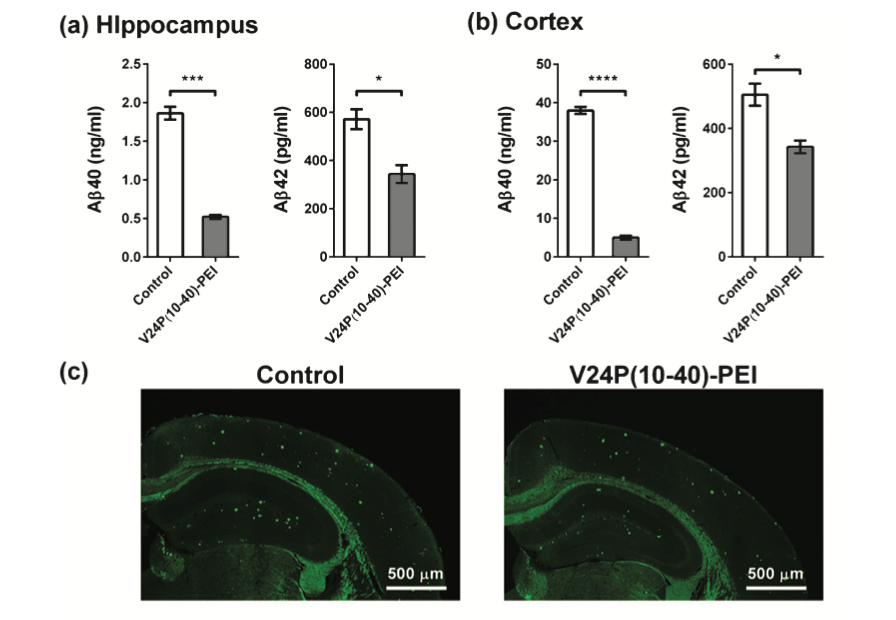
Several studies show that V24P (10-40) PEI decreases the accumulation and toxicity of both Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the hippocampus and the cortex of AD mice models (see Fig.2).[3,5] V24P (10-40) PEI peptide also significantly decreases the amyloid-β plaque aggregation in AD mice models.[7] It is well known that amyloid-β plaques and neurofibrillary tangles tend to accumulate in the olfactory bulb, damaging olfaction in the early stages of AD. [3] This novel peptide demonstrated that it could reduce both plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the olfactory bulb.[3,6] For this reason, the V24P (10-40) PEI peptide is an excellent candidate for preventing the pathogenesis of AD from its early stages.[1-4]After testing different quantities (mg) of V24P (10-40) PEI, the investigators found that administering 1.6mg 6 times a week for eight months can reduce the amyloid-β in the hippocampus by 81%.[3] When comparing those results with other peptides made specially for decreasing the amyloid-β in the hippocampus, V24P (10-40) PEI shows the best performance (see Table 1).[3] Several studies suggest that V24P (10-40) PEI has excellent potential in slowing down the pathogenesis of AD by trapping and eliminating the overexpressed amyloid-β peptides in the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, brain cortex, and other possible areas.[2-4] AD is known to be a multifactorial disorder. However, a large percentage of patients show amyloid-β aggregation postmortem.[5] V24P (10-40) PEI is one of the few peptides tested in vivo, showing excellent results in decreasing self-aggregate proteins in the brain. [3,6] Stabilizing the amyloid-β levels in the brain can reduce neuronal cell mortality and memory loss, decreasing the chances of developing AD. [2]
Results of the Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in the (a) hippocampus and (b) the cortex after the administration of V24P (10-40) PEI peptide